Content marketers love to toss around buzzwords.
From going after low-hanging fruit to growth hacking your way into existence, these terms have truth to them, but the meaning gets lost if overused.
SEO has become a buzzword too. People who don’t truly understand the term and its requirements use it to impress clients or prove credibility. As an agency that offers SEO services and has an emphasis on SEO-focused content marketing, these people make us look bad.
To set the record straight, we decided to go back to the basics. Here is a guide on what SEO content actually is, why your business needs it and how to create optimized content that Google will rank.
What is SEO Content?
SEO content is content written with the intent of ranking on a search engine like Google. SEO stands for “search engine optimization.”
There are certain elements such as keywords, site structure and copywriting that search engines look at to determine if a piece of content fits what the searcher is looking for. If your content isn’t properly optimized, the search engine won’t rank your content in the top results.
Google’s ranking algorithm has changed over the years, but website content is a consistent factor. When looking at the impact of content as a ranking factor, a study by Moz weighted page-level keywords and content features at 15 percent importance and a more recent study weighted on-site content as 18-21 percent importance. So, while a website’s technical structure should be optimized for SEO, creating well-structured content is also key.
SEO Content Helps Businesses
There are many reasons to create content. Some posts may be used to boost your credibility in the industry while others are used to build links to your website. SEO content does a little of both, and can significantly increase your website traffic along the way.
Boosts Organic Traffic
Creating SEO-driven content that ranks will drive organic traffic to your website. You can see this happen in any industry.
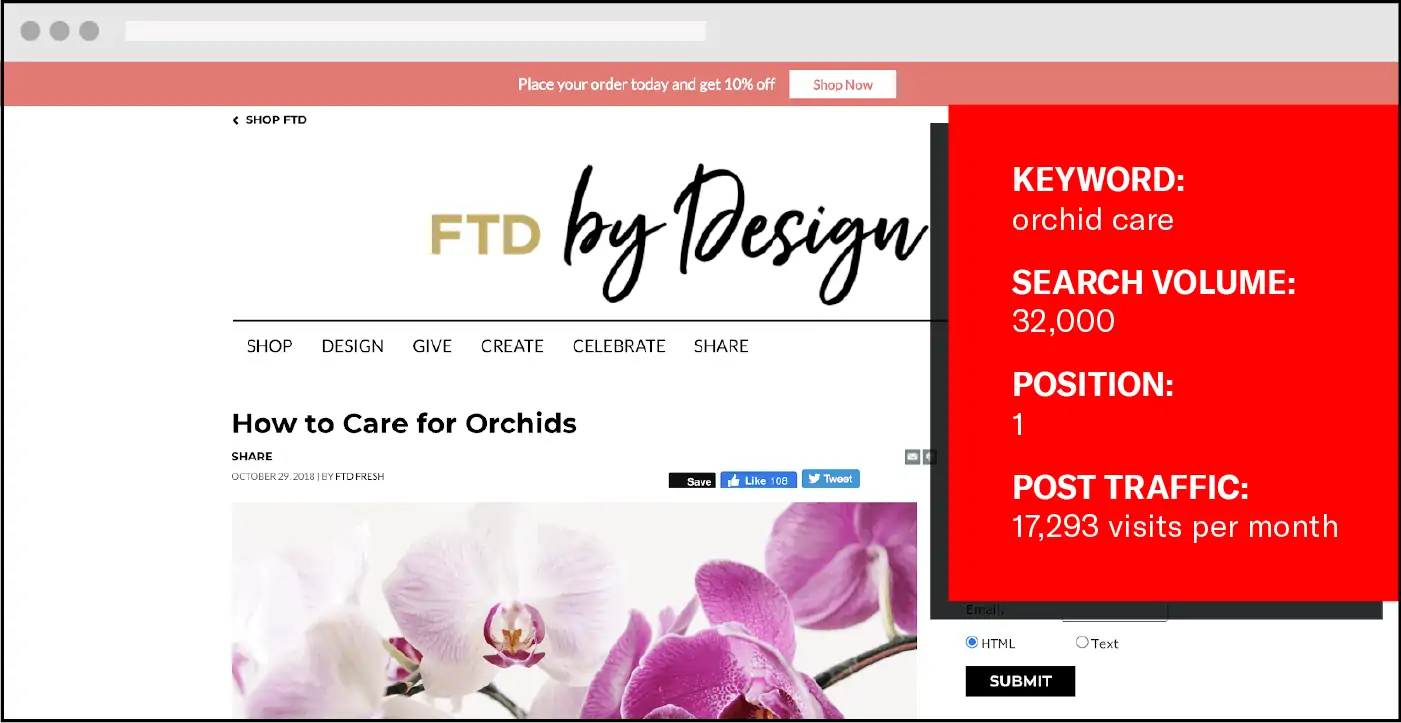
In the floral space, the keyword “orchid care” has 32,000 monthly searches. The FTD post ranking #1 drives monthly organic traffic of 17,293 visits per month.
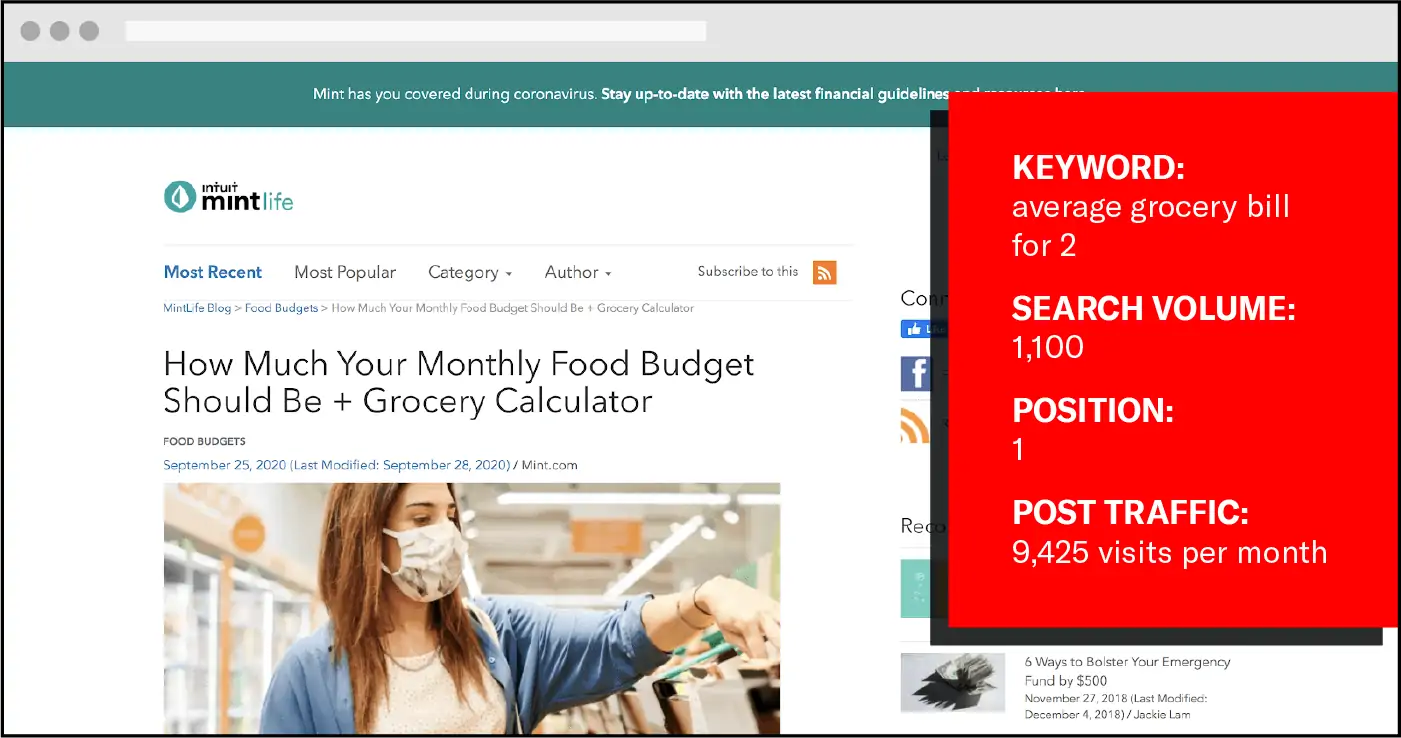
When looking at the finance industry, the keyword “average grocery bill for 2” has 1,100 monthly searches but the top result drives monthly organic traffic of 11,400 visits per month.
Not all posts will earn the first placement on Google, but ranking on page one, in general, will still increase your organic traffic.
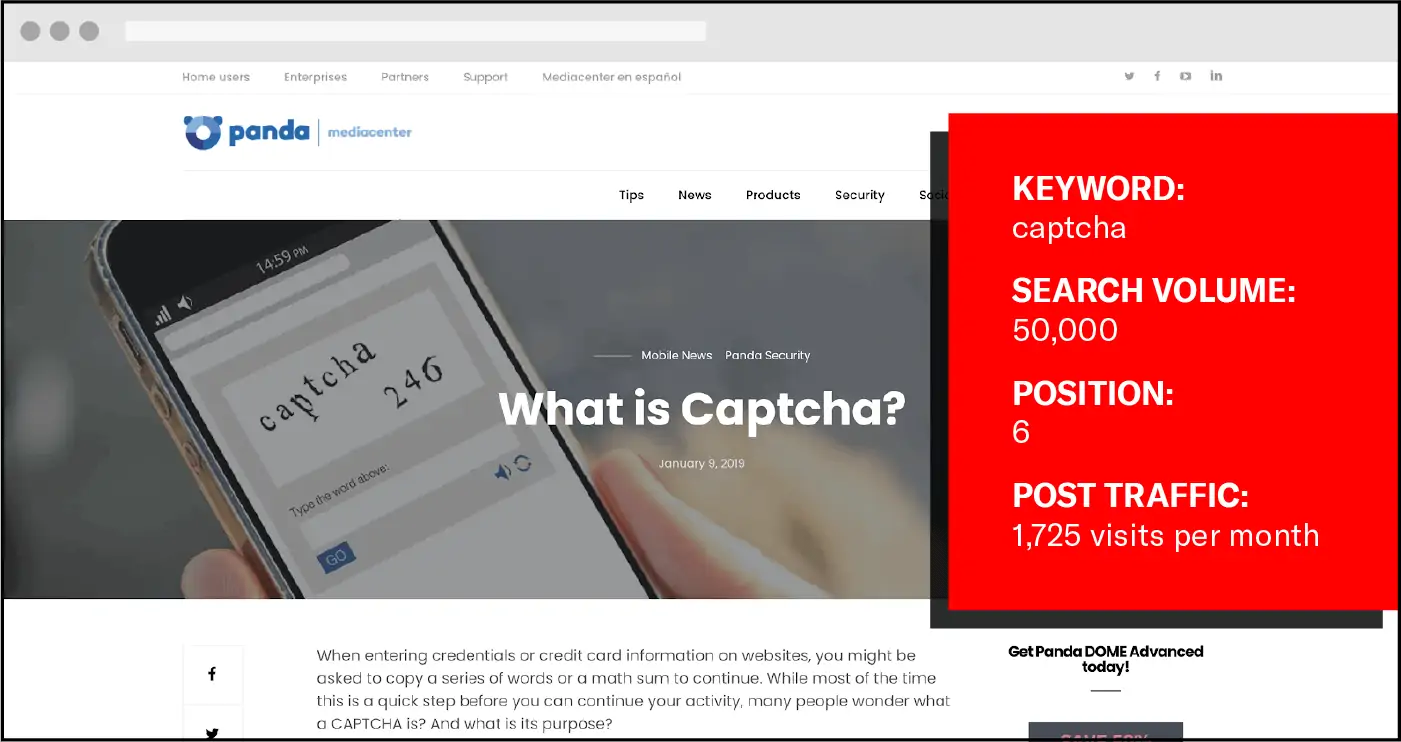
Looking at the cybersecurity industry, the keyword “captcha” has a search volume of 50,000 and is very hard to rank for. The post ranking number 6, still drives 1,725 visits per month.
So as you can see, individual posts that rank on Google can greatly contribute to a site’s overall organic traffic.
Raises Brand Awareness
Brand awareness is not easily measured but is a large contributor to a brand’s success. If no one has heard of you, how do they know they need your product?
Creating SEO content around your brand’s product or service will help you increase your brand awareness. If your content is ranking on Google, more users are clicking on it and familiarizing themselves with your offering.
This brand awareness can be created by layering your content topics. For example, if you provide an apartment search resource, your content can target users before they even search “apartments for rent.” By focusing on terms like “notice to vacate” or “how to get an apartment with bad credit” you are layering content around your apartment search product page. People will reference your guides and earn your trust before they are ready to find a new apartment. Then when they begin their search, your brand will come to mind.
Attracts Top and Middle-Funnel Customers
It’s hard to have a marketing conversation without bringing up the funnel. And while tofu is not part of my diet, it has made it into my SEO strategy. In fact, top-funnel content can be more valuable than the bottom-funnel topics you might have been focusing on.
Creating content that targets broader terms can catch users in the awareness and consideration stage. This gives you an opportunity to guide them to a solution (hint: it’s your product).
Earns Passive Links
You want to work smarter not harder, right? Creating content that’s optimized to rank can help you obtain passive links over time.
If Google thinks your content is good enough to rank, bloggers and reporters will think it’s good enough to cite in their articles. Specific categories of SEO content that we’ve seen do well at earning passive links are statistics posts, definitional posts, resource lists and cost calculators.
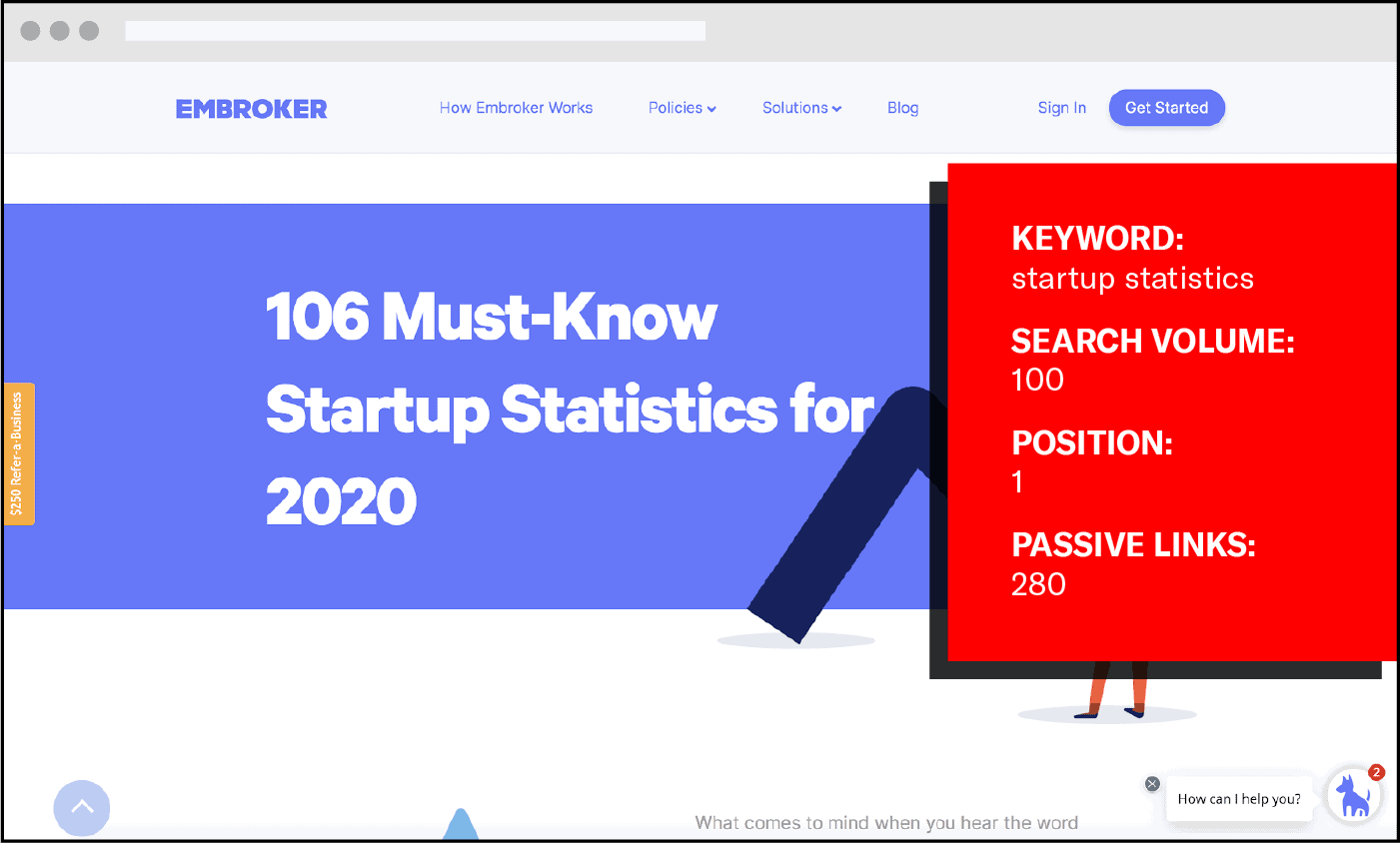
For example, the keyword “startup statistics” only has a search volume of 100, but a website with a domain authority of 58 was able to have their post rank #1 and earned 280 passive links.
Adding shareable assets to these ranking SEO posts will also increase your likelihood of obtaining these passive links.
How to Write SEO Content
So you’ve decided you want your content to rank on Google. Great! Join the club.
Unfortunately, there are many additional factors that will contribute to if you’ll be able to get your post on page one. Your domain authority, site speed and site structure are among the many factors that will impact your ranking.
While you might not have control over those elements, you do have the ability to write a solid piece of content. To help, here is a rundown of how to go about writing SEO content.
Step 1. Find a Keyword
Choosing the right keyword to target is essential. You want to pick keywords that have a strong tie to your brand, have decent search volume, are low difficulty and have a search intent you can match with a blog post.
Keyword research is a much larger topic that a whole blog post could be written on, but here are a few strategies for finding keywords:
- Use content marketing tools to see what your competitors are doing. What topics do they cover? What are their top trafficked pages?
- Try using the hub and spoke strategy. Focus on long tail keywords that tie directly back to your product pages.
- Take a look at Google trends. Is there anything trending in your industry that you can speak to?
- Use Answer the Public to see what additional questions people are asking about your topic. Do any of them have search volume?
- Explore Exploding Topics to see what topics have had a recent growth increase.
Step 2. Evaluate the SERP
Once you decide on a keyword you’ll need to evaluate the SERP. The first thing to look for is search intent.
Some types of search intent include:
- Informational intent – the user is searching the term to find information
- Navigational intent – the user is looking for a specific result
- Transactional intent – the user is looking to purchase something
- Commercial investigation – the user is in the market for something but wants to compare options
The type of search intent will dictate whether you should proceed with the keyword or find a different one. SERPs that show navigational and transactional intent will likely require a product page to rank. It’s best to stay away from them and focus on informational and commercial investigation searches.
Another consideration when analyzing the SERP is the types of websites that are able to rank.
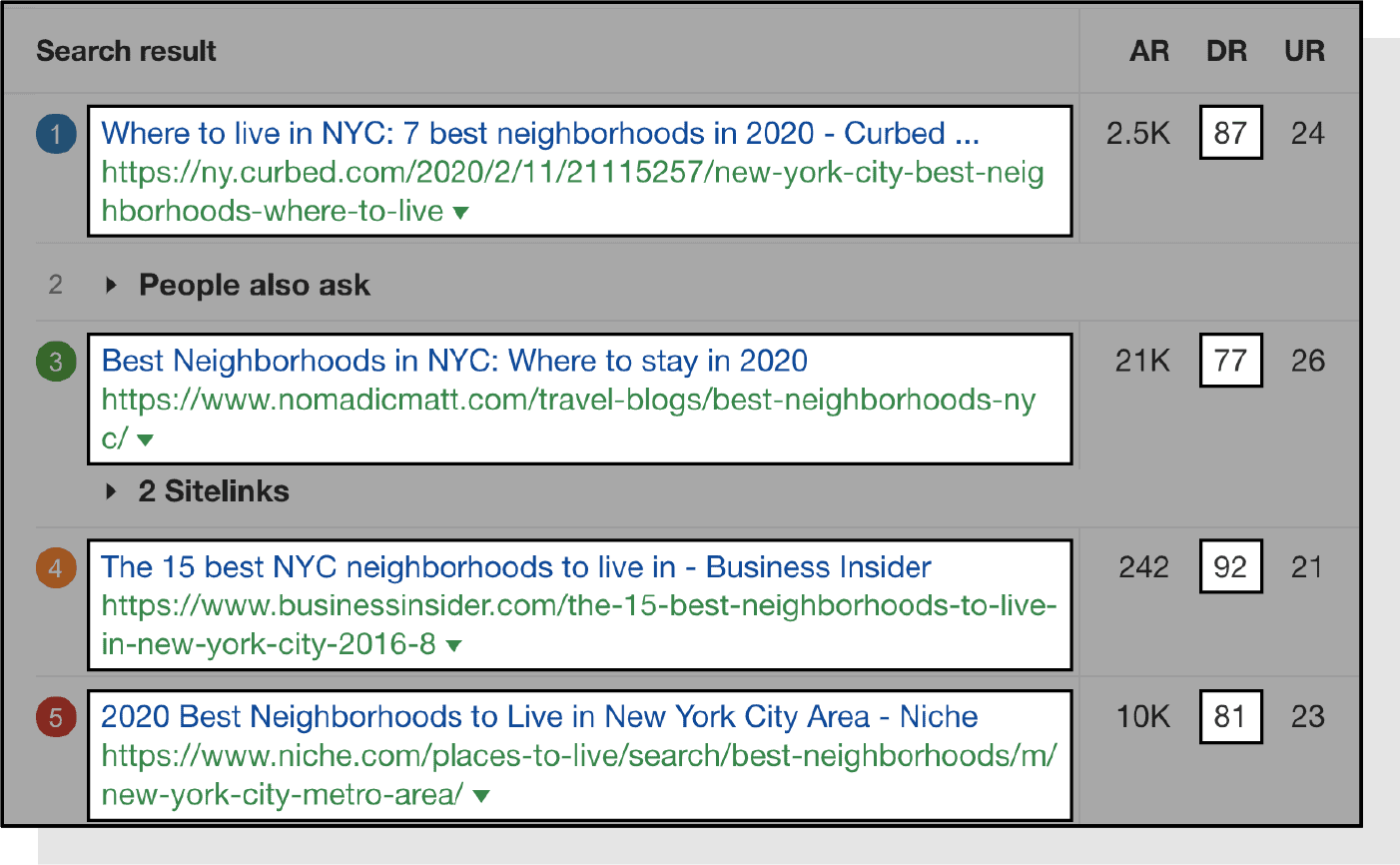
For example, let’s say you’re a real estate brand that’s interested in targeting “best neighborhoods in nyc” which has a search volume of 1,600 and a difficulty of 10.
Looking at the top results, you can see that you’ll need a fairly high DA to rank. You’ll also notice that it’s mainly well-known news and travel sites ranking. As a real estate site, you’ll have a hard time competing.
Step 3. Outline the Post
Once you’ve chosen a keyword and verified that you can compete with the current SERP, you’ll want to outline the post. Outlining a post will help ensure you’re including all the key SEO elements.
For more details on how to correctly structure a post outline, see my previous post on blog post templates. It includes downloadable templates you can use to get started.
There are a number of SEO elements you’ll want to include in your outline:
- A list of your keyword and related keywords
- A blog post title that includes your keyword and will drive CTR
- H2/H3 structuring that will help users find what they’re looking for
- Internal linking to relevant product pages and related posts
Outlining the post will help you naturally include these elements as you write. A well-structured post is also easier for the reader to follow.
Step 4. Write Your Post
After all that, you’re finally ready to write the post.
While you’re writing, be sure to keep your audience in mind. The tone of your piece will depend on what your readers would want to hear. For instance, a post by a cybersecurity company will probably be more technical and direct while a perfume brand might use a more warm and playful tone.
In addition, you’ll want to hold the reader’s attention. Long pages of copy are difficult to read. Keep your paragraphs short (5 lines max) and use visuals to break up the copy.
When writing your SEO content, you’ll want to make it as comprehensive as possible. Ensure you’ve included everything your reader might want to know about the topic. Referencing the People Also Ask questions on Google can help you determine related queries that should be answered in your post. Maybe even try leveling it up with an animated infographic or video.
Check your spelling and grammar with tools like Grammarly or Hemingway. Even the most experienced writers make mistakes.
Step 5. Optimize for SEO
When the post is written and the visuals are created, you’ll be ready to upload to your CMS. WordPress is the most common but other popular options are Wix, Drupal, Squarespace and Weebly.
When you upload, there are additional SEO elements to take into consideration:
- Optimize your URL structure so it includes your keyword
- Include an optimized meta description
- Choose a relevant category for your post
- Create alt text for any images
- Ensure all your links open in a new tab
- Use the Yoast plugin to help you optimize but don’t feel obligated to get every post “in the green” – some requirements aren’t necessary.
Download an SEO content checklist here:
Step 6. Track Your Results
Once your post is live, you can start to track your results. Keep in mind, with SEO you’re playing the long game. Posts can take a few months to a year to start ranking.
If you continue to target attainable keywords and optimize for SEO, you should start to see an increase in traffic to your site, grow your brand awareness and gain passive links.
Keep Learning
There you have it. The next time someone mentions SEO but their content doesn’t follow this basic structure, you’ll be able to call their bluff.
Learning more about these content marketing topics can help you understand who knows what they’re talking about and who is just regurgitating buzzwords. For more information on how to level up your SEO knowledge and get content ranking faster, check out our online SiegeLearn content marketing course.